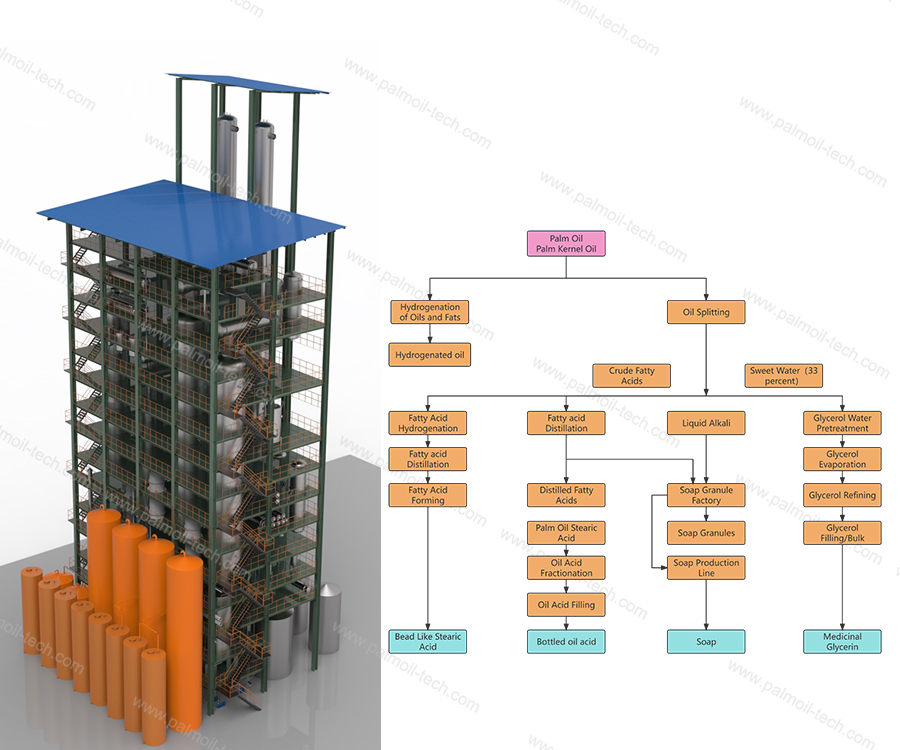
The main components of all animal and vegetable oils are triglycerides and glycerol. The oils are hydrolyzed under high temperature and high pressure to separate fatty acids and glycerol. The crude fatty acids obtained are distilled and fractionated to produce fatty acid products of different components. Glycerol as a by-product is concentrated and purified to obtain 99.7% refined glycerol.
Fatty acids, as the basic products of oil and fat industry, are widely used in various industrial fields, with broad market prospects, and are an important direction for investment in oil and fat industry refining.
The raw materials of the oil and fat fatty acid industry come from a wide range of sources. Palm crude oil, coconut oil, palm kernel oil, UCO, stearin, and other oil products of various qualities can be used as raw materials.
The products vary according to the different components of the oils. Palm oil and palm kernel oil, as the main raw material sources of fatty acid products, occupy an absolute position in the fatty acid industry.
Introduction to the main processes of fatty acid engineering:
Hydrolysis chemical equation
1. Oil hydrolysis
Hydrogenated oil (oil) is input from the bottom of the high-pressure hydrolysis kettle by a high-pressure feed pump, and condensed water is input from the top of the hydrolysis kettle by a high-pressure water inlet pump. Since hydrogenated oil (grease) or hydrolyzed fatty acids are lighter than water or sweet water, hydrogenated oil (grease) or hydrolyzed fatty acids move upward, while water or sweet water (dilute aqueous solution of glycerol) moves downward. The two are in countercurrent contact in the tower kettle, and high-pressure steam replenishes steam and energy from different positions in the middle of the high-pressure hydrolysis kettle, thereby reaching the temperature and pressure of the reaction between oil and water, and realizing the process of continuous hydrolysis. The hydrolyzed crude stearic acid (fatty acid) enters the crude acid storage tank through a pump after flash evaporation, vacuum dehydration and cooling from the top of the tower, and the sweet water enters the pre-concentration first effect kettle for concentration after flash evaporation.
2. Fatty acid distillation
After the hydrolyzed crude fatty acids or hydrolyzed black soap stock crude acid reach a certain degree of hydrolysis, they are pressed into the crude acid storage tank. After the water separated by the crude acid is discharged, the material is pumped into the crude acid metering pot, and after heat exchange with the collected material, it is heated by the heater and enters the distillation tower. The tower kettle material is circulated and heated by the pump through the re-boiler. After the collected materials are condensed by the condenser, part of them flows back to the tower , and part of them are heat exchanged in the crude acid metering pot, and then collected in the metering pot through the cooler. According to the quality requirements of the finished product, they can be input into different storage tanks or directly pumped into the packaging workshop through the collection and delivery pump. Fatty acids are adjusted and mixed in the fatty acid finished product tank and then pumped into the fatty acid storage tank, and then canned or filtered by the filter and input into the user tank.
Hydrolyze crude fatty acids, cut out the part below C14 at the top of the first tower, enter the buffer tank, and can be pumped into the palm kernel oil distillation section; the bottom product enters the second tower, and the second tower separates C16\C18; the top C16 product (1690) of the tower, the bottom C18 product enters the third tower, the top of the third tower is the C18 product (1865), and the bottom of the tower is the black foot entering the black soap stock storage tank.
3. Sweet water concentration
The treated sweet water is pumped from the storage tank through the preheater and the three-effect residual gas, and then input into the first-effect evaporator. The first-effect liquid is pumped to the first effect for circulation; the steam heater is used for circulation heating. The first effect enters the second-effect evaporator through the liquid level automatic control system. The second-effect liquid is pumped and circulated with the first-effect secondary steam. The second effect enters the three-effect evaporator through the liquid level automatic control system. The three-effect liquid is pumped and circulated with the second-effect secondary steam; the pump is pumped and circulated with the glycerol cooler and the black foot cooling tank. After the three-effect liquid level reaches the specified value, the pump is discharged to the glycerol feed storage tank through the three-effect liquid level automatic control system.
The concentrated four-effect evaporator is fed from the treated crude glycerol storage tank, and can also be fed from the first, second, and third effects. The liquid is pumped through the tail gas heat exchanger for circulation heating, and the gas phase is connected to the three-effect vacuum system through the condenser. The discharge concentration is controlled by controlling the discharge speed, and the material is discharged to the glycerol feed storage tank.
4. Glycerol distillation
The concentrated crude glycerol is preheated from the glycerol feed pump through the finished product heat ex-changer, then enters the fraction second heat ex-changer and enters the vacuum degassing tank. Part of the condensed water and other impurities are cooled by the condenser, and the crude glycerol raw material is fed to the glycerol distillation tower through the circulating feed pump, heated and evaporated by the re-boiler, and the heating heat transfer oil is circulated through the heat transfer oil circulation pump. The bottom material is circulated and heated by the circulation pump. The top steam of the tower is condensed by the condenser and enters the collection tank to remove the sweet water treatment section. The glycerol collected from the upper part of the distillation tower passes through the buffer tank and then through the re-flux pump to the top of the distillation tower for re-flux. In this process, it passes through the heat ex-changer and cooler to cool to about 100℃. The glycerol collected in the middle part flows into the re-flux liquid storage tank, and then part of it is pumped into the lower part of the tower for re-flux; the rest is input into the decolorization buffer tank and decolorized by the decolorization delivery pump fixed bed decolorization tower. After decolorization, it first passes through a bag filter and then a precision filter. The finished glycerin enters the packaging intermediate tank, and the problematic product returns to the decolorization intermediate tank. The glycerin black feet discharged from the glycerin tower are input into the glycerin black foot distillation kettle. The heating system consists of a steam generator, a water replenishment plunger pump, and a soft water storage tank. The distilled fraction of the black foot distillation kettle is condensed by a condenser and enters the crude glycerin degassing tank for re-distillation or collection decolorization and desweetening treatment section according to the actual quality. The steam at the top of the distillation tower is condensed by a condenser, and the cooled material is transported to the sweet water treatment section for treatment.
5. Hydrogenation
The oils (fatty acid) is heated by the heater from the raw material storage tank to the finished product heat ex-changer after the feed pump exchanges heat with the raw material storage tank. After the material is dehydrated and deodorized in the degassing tank through circulation, a certain amount of material is diverted into the catalyst configuration tank to dissolve the catalyst from the catalyst hopper and the auger. The dissolved catalyst is pumped into the hydrogenation reactor through the catalyst feed pump. After degassing, another part of the material is sent from the reaction feed pump to the raw material finished product heat ex-changer and then heated by the feed heater and enters the hydrogenation reactor at the same time as the hydrogen from the separation tank. The reacted material is cooled by the raw material finished product heat ex-changer and enters the hot hydrogen separator. The material enters the filter tank from the hot hydrogen separator through the buffer tank. The hydrogen separated by the hot hydrogen separator is separated again by the separator and condensed by the hydrogen condenser before entering the separator. It is then compressed by the hydrogen circulation machine and sent to the separator for recycling. The insufficient hydrogen is sent to the hydrogen buffer tank by the pressure swing adsorption through the hydrogen compressor, and then sent to the separator from the hydrogen buffer tank through the regulating valve. The material in the filter tank is pressed into the sealed filter by the filter press pump and filtered, and then sent to the finished product storage tank, and then sent to the next production section by the finished product delivery pump.
6. Oleic acid separation
The fatty acids are pumped into the crystallizers and partially crystallized by cooling to the required temperature, and the remaining liquid portion is separated from the solid portion by a pattern filter press;
The fatty acids first flow into one of the crystallizers, where they undergo a full crystallization cycle. Once the liquid level in the crystallizer reaches a high level, the feed is stopped and the fatty acids in the crystallizer are heated to melt the residual crystals inside. This is done to convert the fatty acids in the crystallizer into liquid form in order to ensure uniform nucleation and a controlled crystallization process.
Next, crystallization begins with controlled cooling. Each crystallizer is equipped with a water jacket, a stirrer, and a control valve that regulates the cooling cycle.
When the cooling cycle is complete, the fatty acid slurry is discharged into a membrane filter press for solid-liquid separation. The crystallized phase or stearic acid fraction remains in the filter tank, while the filtrate or oleic acid fraction flows through the designed channels and is collected in the oleic acid tank.
When the back pressure of the filter press increases to a certain set value, the stearic acid mass is squeezed to remove the remaining oleic acid fraction. Then it is discharged from the filter and enters the stearic acid melting tank for melting operation.
7. High tower granulation
The material is pumped into the finished product storage tank through the finished product storage tank in the packaging room, and pumped into the top distributor of the tower by the material pump for spray granulation. The liquid particles are cooled by air and heat exchanged with cooling water to become solid bead particles. The flow is intercepted on the fluidized bed and discharged to the vibrating screen for classification. The qualified products enter the weighing scale for measurement and packaging, and are stored by forklift after the pallet is full. The unqualified products are melted through the pipeline and enter the waste storage tank and return to the system.